Section 19.3 Plane Mirrors
The ray model for light can be used to understand how images are created in plane mirrors.
Subsubsection Key Ideas
Images are produced by intersecting light rays and can be seen all over the natural world.
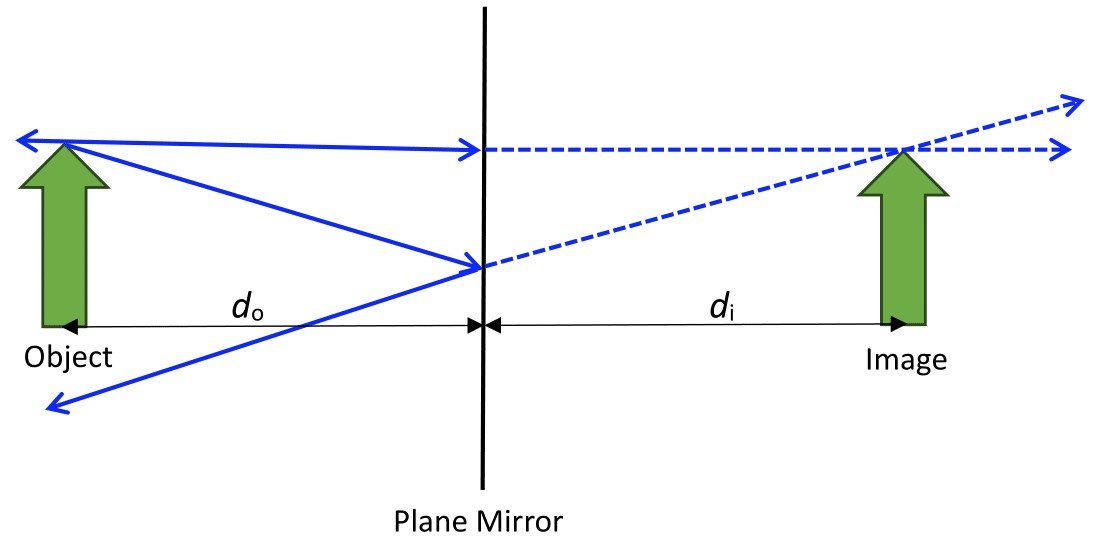
Principle 19.3.3. Image Distance.
If you measure from the surface of the mirror, the distance of an object to the mirror is equal to the negative of the distance of the image to the mirror: \(d_o = -d_i\)
In this situation, you are seeing a virtual image. These types of images are produced when light rays do not physically travel to the image location. When you are looking at yourself in a mirror, there is no physical copy of yourself behind the mirror. The image that you see is virtual. When you are looking at ray diagrams of mirrors and lenses, you are typically interested in figuring out where the image is located.
Definition 19.3.4. Virtual Images.
A Virtual Image is created when light rays do not travel through the image location. These images will have a negative image distance.
Subsubsection Plane Mirror Activities
Checkpoint 19.3.5. Plane Mirror Simulation.
Spend some time playing with this
simulation. Click on the "Mirror" option. At the top of the screen, select the flat mirror option.
Make some observations as you move the object away from and towards the mirror.
Checkpoint 19.3.6. Mirror Illusion.
Watch this video about a supposed “mirror illusion”.
Answer the following questions:
-
What is the illusion here?
-
Draw a ray diagram to explain how you can still see the object in the mirror.
-
How would you explain this to someone that doesn’t know anything about the ray model for light and reflections?
References References
[1]
"HOW does the MIRROR know this? 😳😨 #Shorts." YouTube, uploaded by Cam Casey, 7 April 2023, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gNgSlGn59xA&ab_channel=CamCasey
