Skip to main content\(\newcommand{\N}{\mathbb N}
\newcommand{\Z}{\mathbb Z}
\newcommand{\Q}{\mathbb Q}
\newcommand{\R}{\mathbb R}
\newcommand{\lt}{<}
\newcommand{\gt}{>}
\newcommand{\amp}{&}
\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}
\newcommand{\fillinmath}[1]{\mathchoice{\colorbox{fillinmathshade}{$\displaystyle \phantom{\,#1\,}$}}{\colorbox{fillinmathshade}{$\textstyle \phantom{\,#1\,}$}}{\colorbox{fillinmathshade}{$\scriptstyle \phantom{\,#1\,}$}}{\colorbox{fillinmathshade}{$\scriptscriptstyle\phantom{\,#1\,}$}}}
\)
Section 8.10 Force and Potential Energy
Video Lesson 8.10.1. Force and Potential Energy.
Definition 8.10.2. Force and Potential Energy.
Potential energy and the corresponding conservative force are related (in one dimension, \(x\)) by
\begin{equation*}
\vec{F} = -\frac{dU}{dx}\hat{x}
\end{equation*}
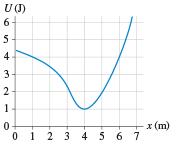
Activity 8.10.1. Practice Diagram.
Below is a potential energy diagram for some system.
(a)
What property of the graph can you use to identify the force that this particle experiences? Explain your reasoning.
(b)
At what position(s) is the force on the particle zero?