Section 28.1 Ampere’s Law
Subsubsection Key Ideas
Definition 28.1.2. Ampere’s Law.
Ampere’s Law relates the net magnetic field around a closed curve to the current passing through the region bounded by the curve:
\begin{equation*}
\bigcirc \!\!\!\!\!\!\!\!\int_S \vec{B}\cdot d\vec{s} = \mu_o I_{enclosed}
\end{equation*}
The integral in the definition above is a line integral. The circle over the integral symbol indicates that this is an integral over a closed path. Ampere’s Law is useful when you are able to identify a symmetry of your current distribution.
Subsubsection Activities
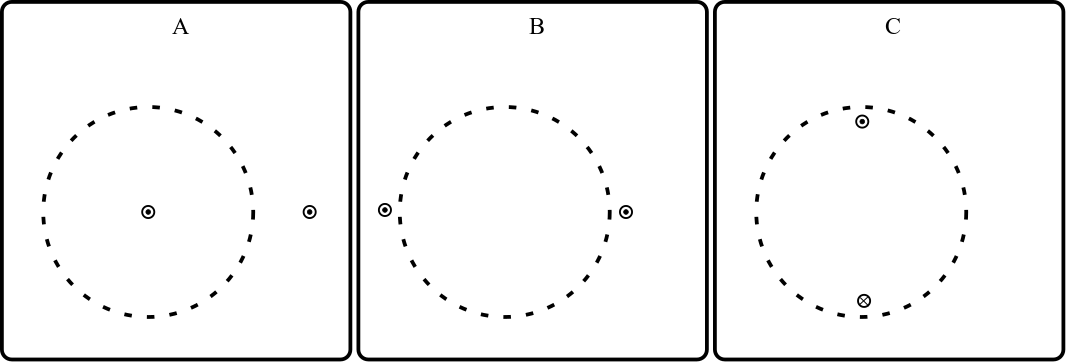
Explanation 28.1.1. Three Loops.
Shown below are three different cases, each with two identical current-carrying wires and a circular Amperian loop. In which case is the net magnetic field around the loop the largest?